





















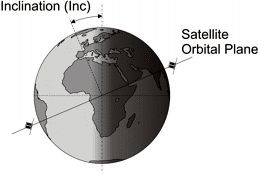
 Inclination:
Inclination:
The angle between the Earth's equatorial plane and the orbital plane is
called inclination and measured relative to the Earth's orbital plane
as shown in the figure. If the inclination lies
between 0° and 90°, it is
called a prograde orbit, as the satellite is moving in an eastern
direction.
An Inclination between 90° and 180° is called retrograde, as the
satellite moves in a western direction.
Right Ascension of the Ascending Node:
The angle between the Vernal Equinox (The X-axis of the ECI frame) and the
line, which is given by the intersection between the orbital plane of the satellite orbit
and the equatorial plane of earth as shown in the next figure.
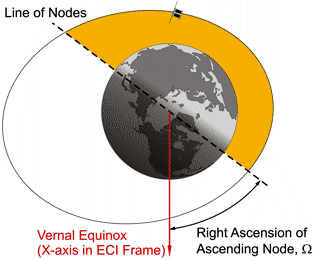
The ascending node is a line given by the two points where a satellite
passes through the Earth's equatorial plane while moving up over the
equatorial plane (Shown on the figure as darkened orbit part) and going down below it again.
Eccentricity:
The eccentricity defines how elliptical
or circular an orbit is. An eccentricity of 0 is equal to a circular
orbit, while an elliptic orbit has an eccentricity between 0 and 1,
a parabolic orbit approximately 1 and a hyperbolic orbit above 1.
Argument of Perigee:
The argument of perigee is the angle between the ascending node (Line of nodes) and perigee as shown in the next
figure.
The Perigee is the line going from center of the Earth to the perihelion.
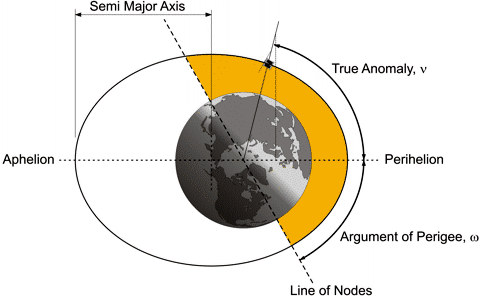 The perihelion is on the opposite side from the
aphelion, which is the point where the satellite is most distant from the center of Earth.
The perihelion is on the opposite side from the
aphelion, which is the point where the satellite is most distant from the center of Earth.
The semi major axis is equal to the largest radius of the elliptic orbit with respect to its center.










 The perihelion is on the opposite side from the
aphelion, which is the point where the satellite is most distant from the center of Earth.
The perihelion is on the opposite side from the
aphelion, which is the point where the satellite is most distant from the center of Earth.